There’s a new sight in the sky these days – the newly-discovered Comet NEOWISE is flying past the Sun. This marks the first time since the 1990s that people have had a chance to see a comet with their bare eyes.
A comet is basically a ball of dirty ice that orbits the sun. As the comets come close to the sun, the sun melts some of the ice, which forms a tail behind the comet as it flies through space.
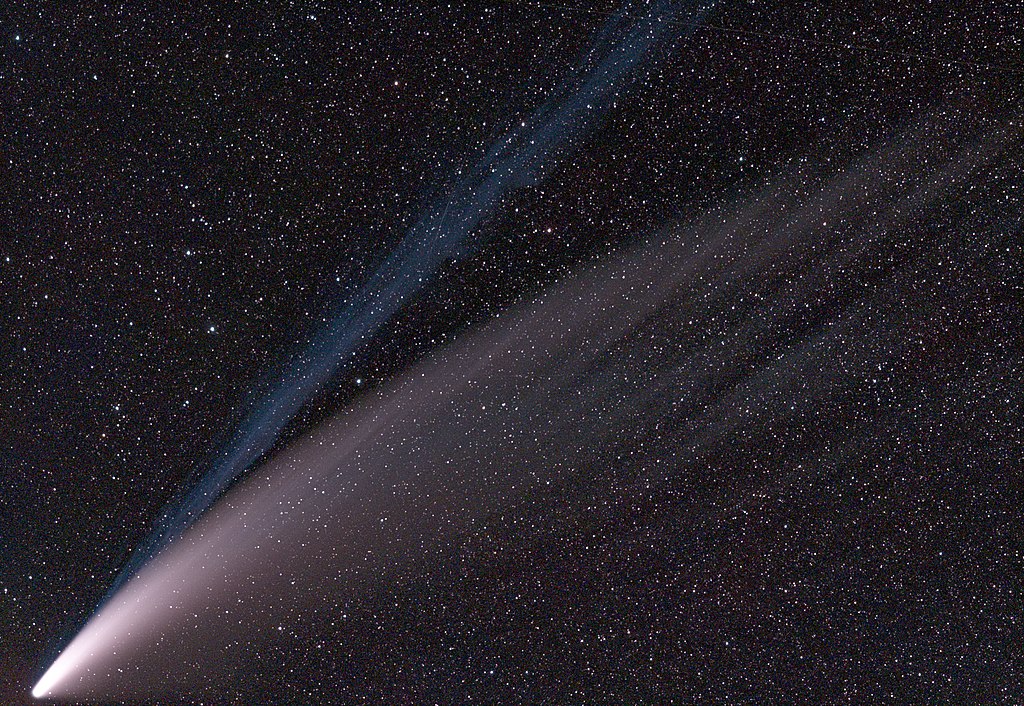

(Source: SimgDe [CC BY-SA], via Wikimedia Commons.)
Most comets have an orbit that looks like a flattened circle. Comets spend most of their time moving slowly, far away from the Sun. As they pass the Sun, they speed up.
The size and shape of a comet’s orbit affect how long it takes to complete its orbit. Halley’s comet is a famous comet that comes around once every 75 years. But the orbit of NEOWISE is so flat and stretched out that the last time it was here was about 6,800 years ago.
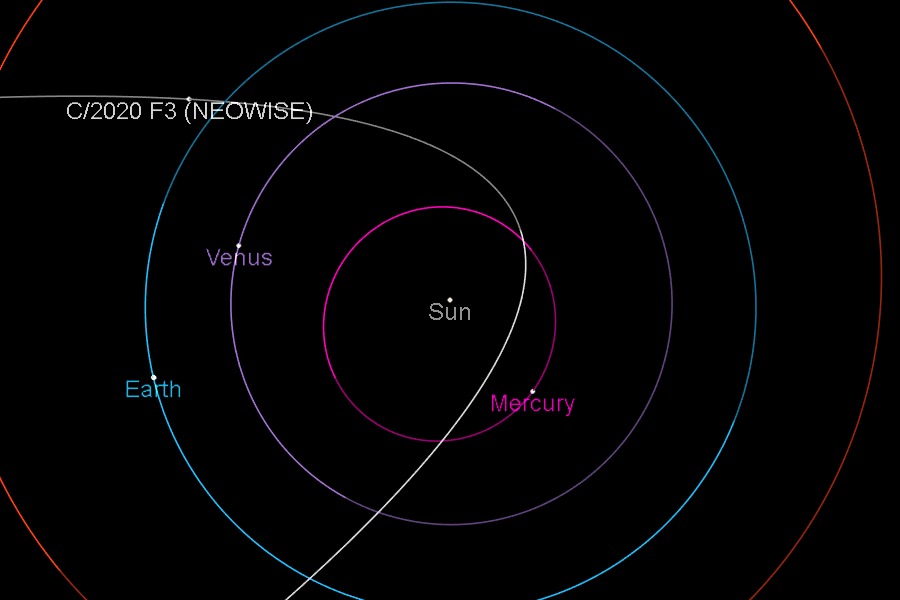
Because of the long time it takes to orbit, NEOWISE was only just discovered a couple of months ago. It was spotted in March using a special space telescope run by NASA.

(Source: Courtesy NASA/JPL-Caltech. [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons.)
The name of the telescope system that first spotted the comet is NEOWISE (Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer), so that’s how the comet got its name. Its official name is even less catchy – C/2020 F3.
It’s not exactly true that the comet was just discovered. People almost certainly saw NEOWISE around 6,800 years ago, but that was before humans had even invented writing, so there are no records of it passing.
(Source: NASA [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons.)
NEOWISE is easy to see now because it’s close to the Sun. At its farthest, NEOWISE will be 630 times farther away from the Sun than Earth is. (If you want to do the math, multiply the distance between the Earth and the Sun – 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) – by 630.)
NEOWISE actually has two tails. One tail is made of bits of ice melted flying off the comet. The second tail is made of plasma – gas that is charged with electricity. That’s similar to the idea behind a neon light.
The icy tail flows straight behind NEOWISE, but the plasma tail is bent toward the Sun because of the Sun’s magnetic field.
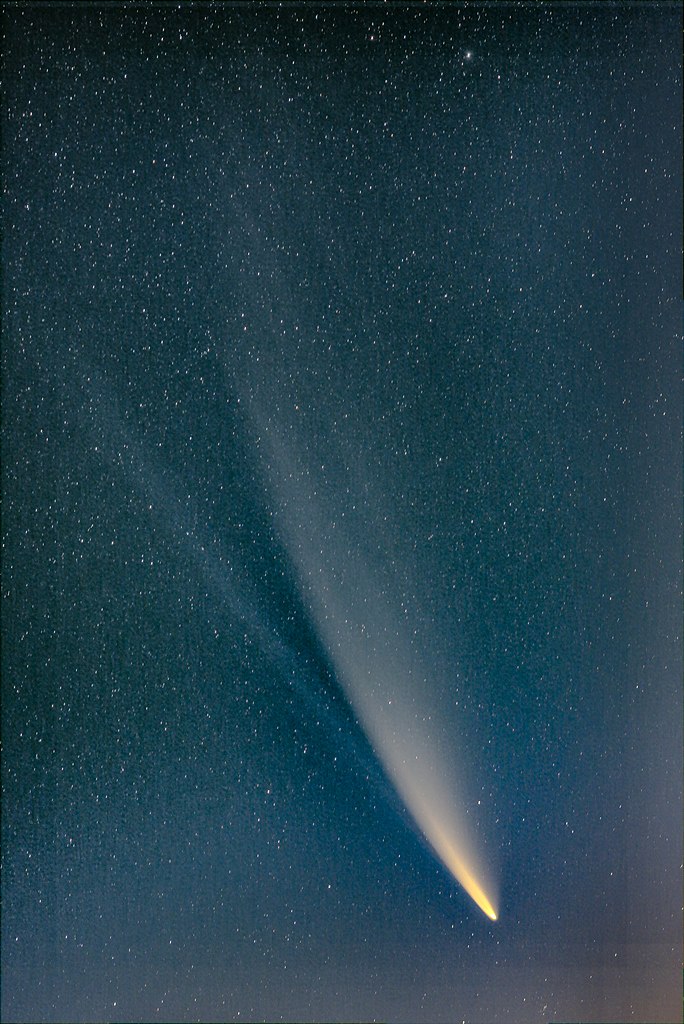

(Source: Andy.niko [CC BY-SA], via Wikimedia Commons.)
Even at its closest – which will be on July 23 – the comet will still be as far away from the Earth as Mars is. But it should still be bright enough to see, even without binoculars or a telescope.
The comet’s brightness will depend on how big the icy tail grows. Lots of ice particles reflecting the Sun’s light could make the comet even brighter.
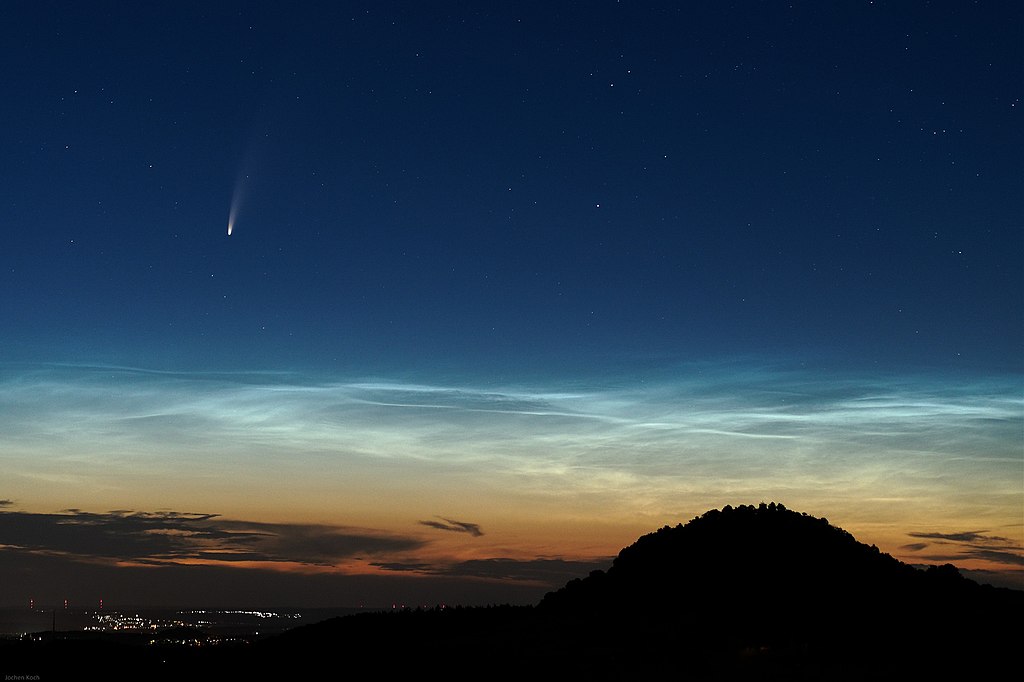

(Source: JochenK2002 [CC BY], via Wikimedia Commons.)
The comet is visible in the northern hemisphere (half of the world). The best time to view it is about an hour and a half after sunset, low in the northwest sky. It should be just below the constellation (group of stars) known as Ursa Major (the Big Dipper).

(Source: Alex Zelenko [CC BY-SA], via Wikimedia Commons.)
Did You Know…?
Though you won’t need any special equipment to see Comet NEOWISE, you’ll get a much more detailed view if you are able to look at it with binoculars or a telescope.
