When heat waves on land cause wildfires, people see them and notice them. But scientists are warning that heat waves in the oceans may be causing as much or more damage.
Global warming has caused the temperature of the world’s oceans to go up much faster than expected. Because about 93% of the heat from global warming goes into the oceans, sea temperatures are rising far more quickly than land or air temperatures.
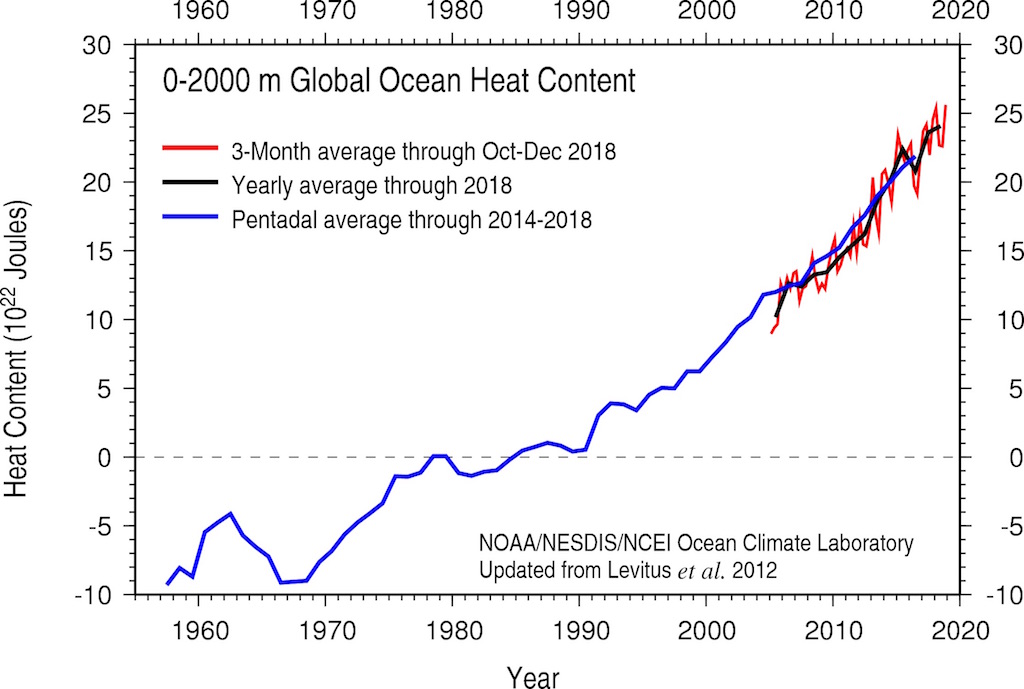
(Source: NOAA.)
A recent study looked at heat waves in the ocean – when temperatures reached a very high point and stayed there for five days or longer. The study showed that the heat waves are happening more often, lasting longer, and having more serious effects than any time recently.
In the last few years, the number of heat wave days has tripled. And the number of heat wave days per year in the last 30 years is more than double the number from over 60 years ago.
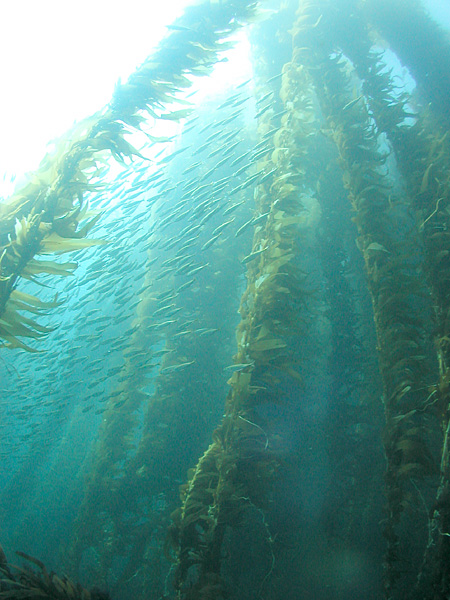

(Source: Aquaimages [CC BY-SA 2.5], via Wikimedia Commons.)
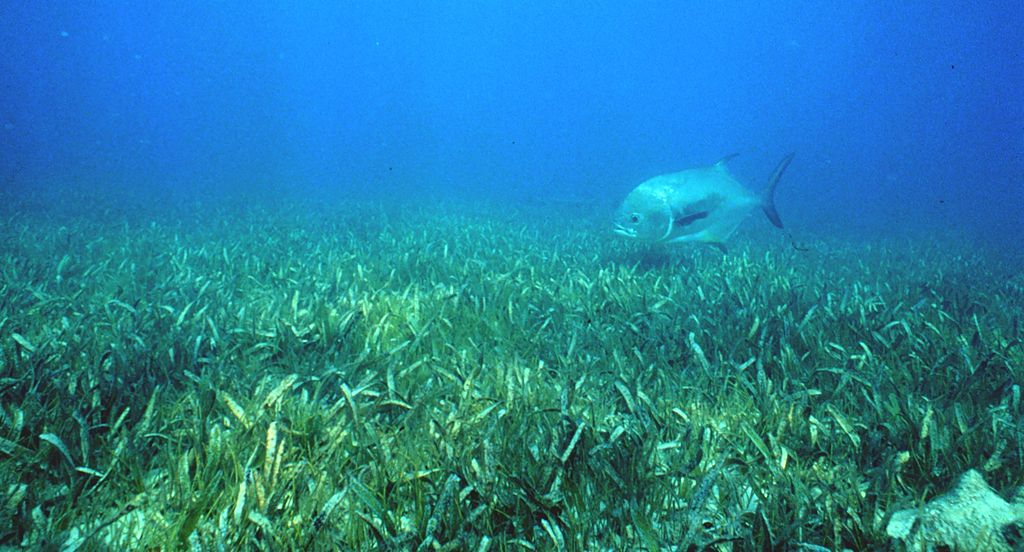
Heat waves have terrible effects in the oceans. Hidden under the ocean’s surface, there are huge numbers of plants. There are great forests of kelp and wide fields of sea grass. There are also large coral reefs. All of these have been hit hard by the rising temperatures.
“You see the kelp and sea grasses dying in front of you. Within weeks or months they are just gone, along hundreds of kilometers of coastline,” says Dan Smale, the scientist who led the research.
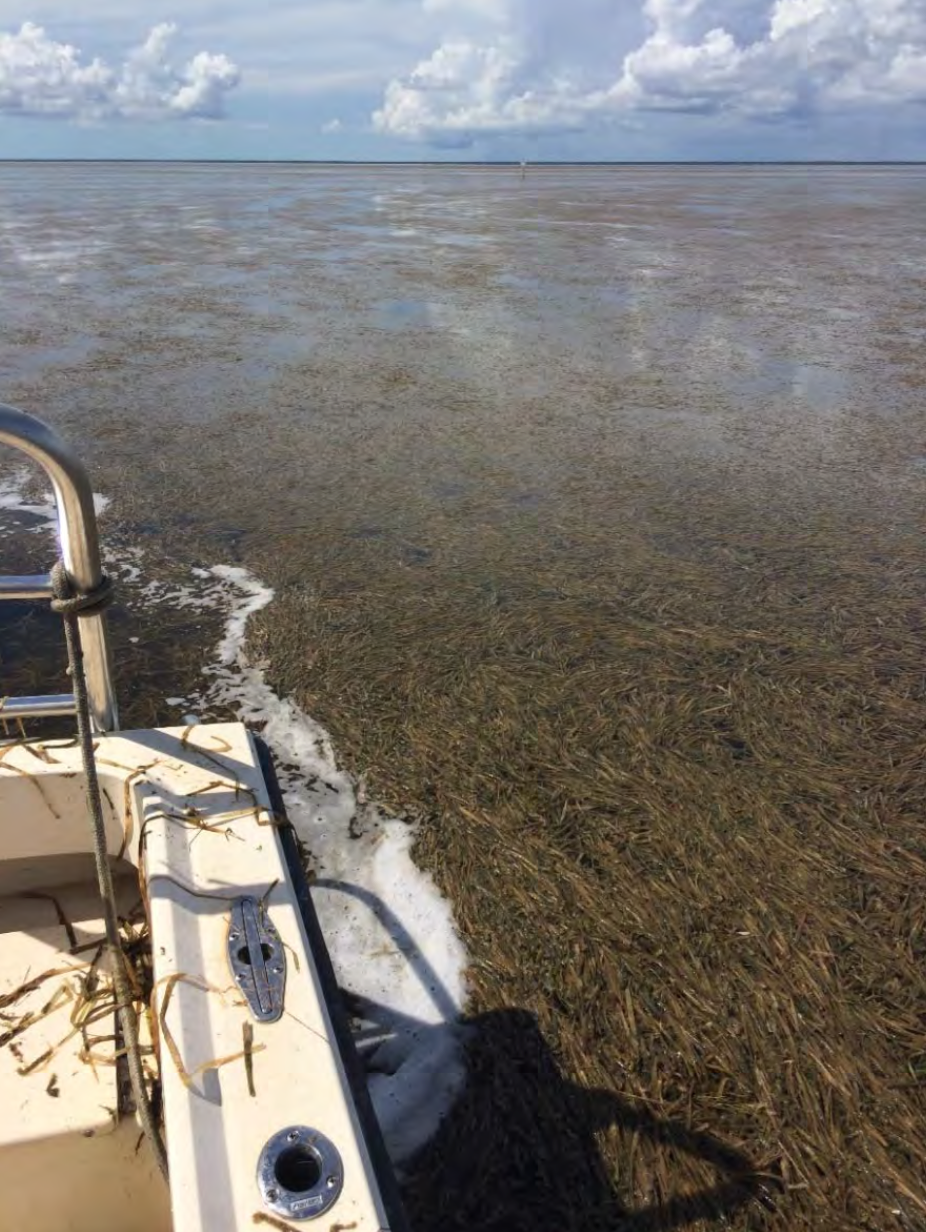

(Source: South Florida Water Management District, via Wikimedia Commons.)
The loss of these plants and corals has a huge effect on life in the ocean – and out of it. Animals, both small and large, that depend on kelp, sea grass, and coral reefs suddenly find the environment they live in destroyed.
Though many sea animals can travel, they may not be able to move fast enough to escape a heat wave affecting a large area. Or they may be unable to find another protected spot. For birds that depend on fish for food, ocean heat waves can be just as harmful.
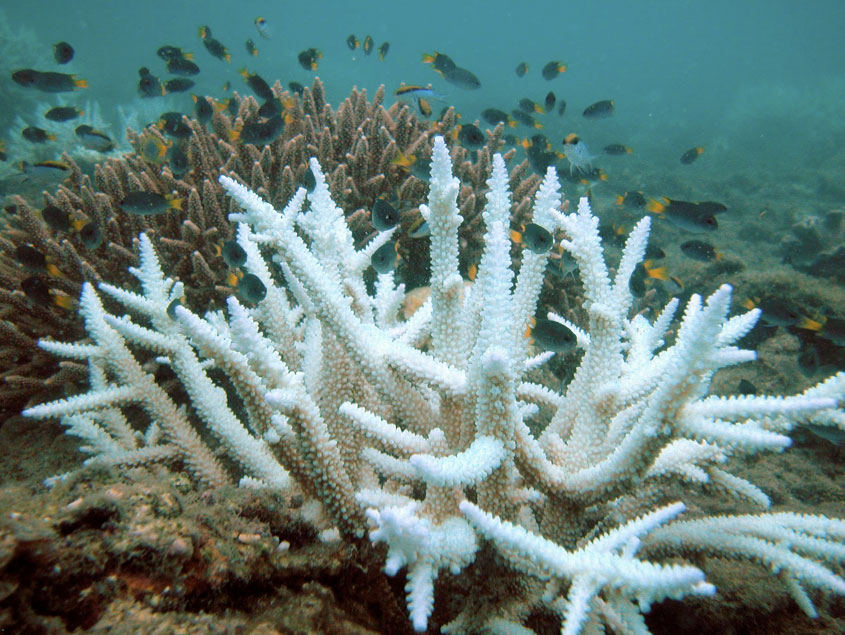

(Source: Wikipedia.org.)
The problems also affect humans. Almost a billion people count on the sea for food or money. Around the world, fewer fish are being caught because there are fewer fish to catch. Controlling global warming could help many more fish survive.

(Source: Masturbius/German Wikipedia, via Wikimedia Commons.)
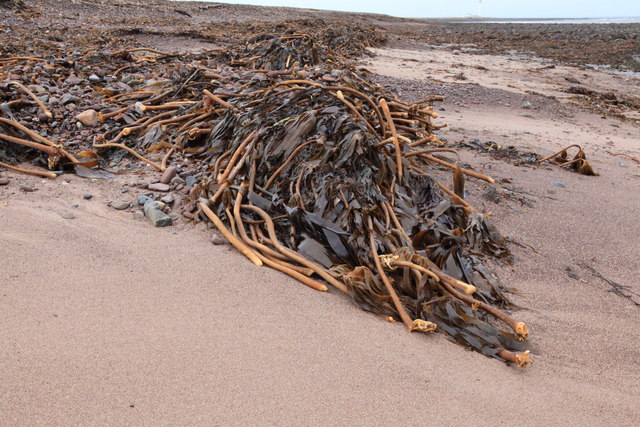
Sadly, the loss of plants in the ocean could make ocean heat waves worse. Polluting gases from human activity, sometimes called “greenhouse gas emissions”, are the main cause of global warming. As humans put more carbon dioxide and other gases into the air, the world heats up.
Plants help by taking carbon dioxide out of the air. Ocean plants are a huge part of this – about 40% of the world’s carbon dioxide is taken in by the oceans. But warmer oceans take in less carbon dioxide than cooler oceans. As huge numbers of plants die off, more carbon dioxide will remain in the air, making global warming worse.

(Source: Calum McRoberts, via Wikimedia Commons.)
Malin Pinsky, who studies ocean warming, but wasn’t part of the study, told the Guardian newspaper, “These events are likely to become more extreme and more common in the future unless we can reduce greenhouse gas emissions.”
