The world is facing a “supply chain” crisis. There are shortages of all kinds of products. And the problem is growing because the materials needed to make new products are either in short supply, or can’t be moved to the places that need them.
These days, if you go to a store near you, you may find some empty shelves. If someone you know has tried to buy something online, they might have been told they have to wait. And prices are going up, even for products that are still available. This is the side of the supply chain crisis that customers see.
😕
This image has not been loaded because of your cookie choices. To view the content, you can accept 'Non-necessary' cookies.
The world is facing a “supply chain” crisis. There are shortages of all kinds of products. The problem is growing because the needed materials are either in short supply, or can’t be moved to the places that need them. Above, empty shelves at an IKEA store in New York.
What’s a supply chain?
A supply chain is how all the parts and services needed to make a product get supplied.
Think about a simple product like a pencil. A company that makes pencils needs at least wood, lead (graphite), glue, metal, erasers, and some paint for the outside of the pencil. Then think about the companies that provide wood, lead, glue, metal, erasers, and paint. They need supplies to make their products, too.
Now think about complicated products, like cars or computers. These have thousands of parts that may be supplied from all around the world. Many of these smaller parts are made in one place and then shipped to another place where they are put together before being sent off somewhere else.
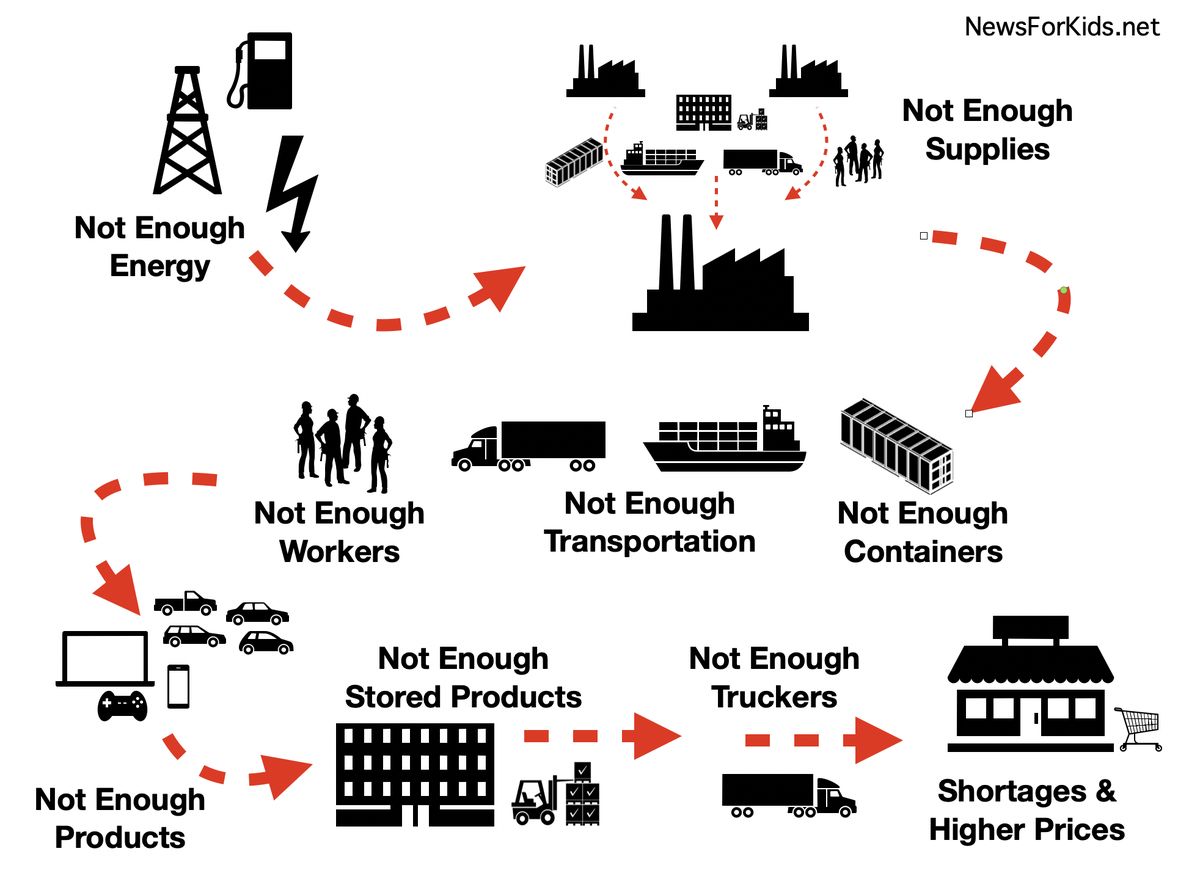
(Source: NewsForKids.net [CC BY-SA 4.0].)
Before the coronavirus pandemic, the world’s supply chain was incredibly complicated, but it worked pretty well. Some companies didn’t even keep big supplies of materials around because they felt sure they could get what they needed in just a few days.
But as different places went into lockdowns, factories closed. Not everywhere and not all at the same time, but enough to start supply chain trouble. China was hit first by the coronavirus. Its factories produce roughly 30% of the world’s products.
Transportation was also affected. In some places, ships weren’t allowed to dock. Many places were short on workers, too. So fewer ships were being loaded and unloaded. Ships started to back up outside of major ports.
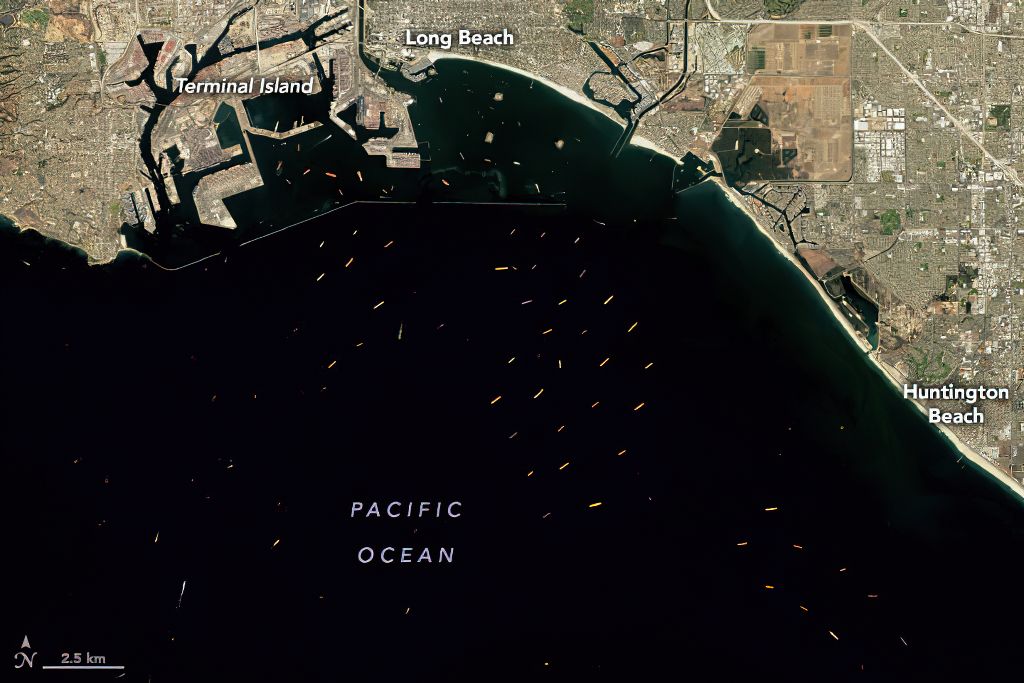

(Source: Joshua Stevens, NASA’s Earth Observatory.)
The world began to run short of the big containers that carry products on ships, trains, and trucks. Without containers, even factories with lots of products had trouble shipping them.
As countries opened up again after the lockdowns, businesses and factories restarted. Customers ordered more and more products – even more than before the pandemic. This sudden, huge demand made the supply chain even worse.
😕
This image has not been loaded because of your cookie choices. To view the content, you can accept 'Non-necessary' cookies.
The world began to run short of the big containers that carry products on ships, trains, and trucks. Without containers, even factories with lots of products had trouble shipping them. Above, containers at the Port of Oakland, California last Thursday.
Factories that make the chips that are so important for electronic devices couldn’t make enough chips. That affected the makers of cars, computers, and other electronic devices, since they depend on these supplies.
Energy shortages are making supply chain problems worse. When factories were closed, businesses that provide coal, oil, and natural gas cut the amount of fuel they produced. But now, in places like China and India, there’s not enough fuel for factories to keep up with the demand for products.
😕
This image has not been loaded because of your cookie choices. To view the content, you can accept 'Non-necessary' cookies.
Factories that make the chips needed for electronic devices couldn’t make enough chips. That affected the makers of cars, computers, and other electronic devices, since they depend on these supplies. Above, the parking lots at two new car dealers were nearly empty in July.
Finally, in many places, there are fewer workers. After the pandemic, many people decided not to return to work. Many businesses can’t find enough workers. A shortage of dock workers and truckers is making it harder to get products where they’re going.
Countries around the world are racing to solve these problems. China is trying to produce more fuel. Chip makers are opening more factories to produce more chips. In the US, two important ports are now running 24 hours a day all week long to unload more ships. Many countries are making efforts to hire more truckers.
😕
This image has not been loaded because of your cookie choices. To view the content, you can accept 'Non-necessary' cookies.
Countries worldwide are racing to solve these problems. China wants to produce more fuel. Chip makers are opening more factories. Two important US ports are now running 24 hours a day. Many countries are trying to hire more truckers. Above, a sign in Reading, England.
Still, experts say it will take time for the world’s supply chain problems to get sorted out. That means that over the next few months, there are likely to be more shortages, and prices will probably keep going up.
