On Saturday, Germany shut down the last of its nuclear power plants, ending a long disagreement over the future of nuclear energy in the country. The move is expected to have an impact on the environment, but could lead to a growth of renewable energy sources.
Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is created by splitting atoms. It’s a dangerous process – built on the science behind nuclear weapons. Nuclear power produces toxic waste which must be handled and stored with great care.
Many people believe nuclear energy is an important tool for fighting the climate crisis. When nuclear power works well, it creates far less air pollution than coal or oil.
But nuclear power always produces radioactive materials. The question is whether humans can safely control, store, and contain these materials, even during wars and unexpected natural disasters.
In response to the climate crisis, some countries are adding more nuclear power plants – especially smaller, more modern ones. Germany is going in the opposite direction.
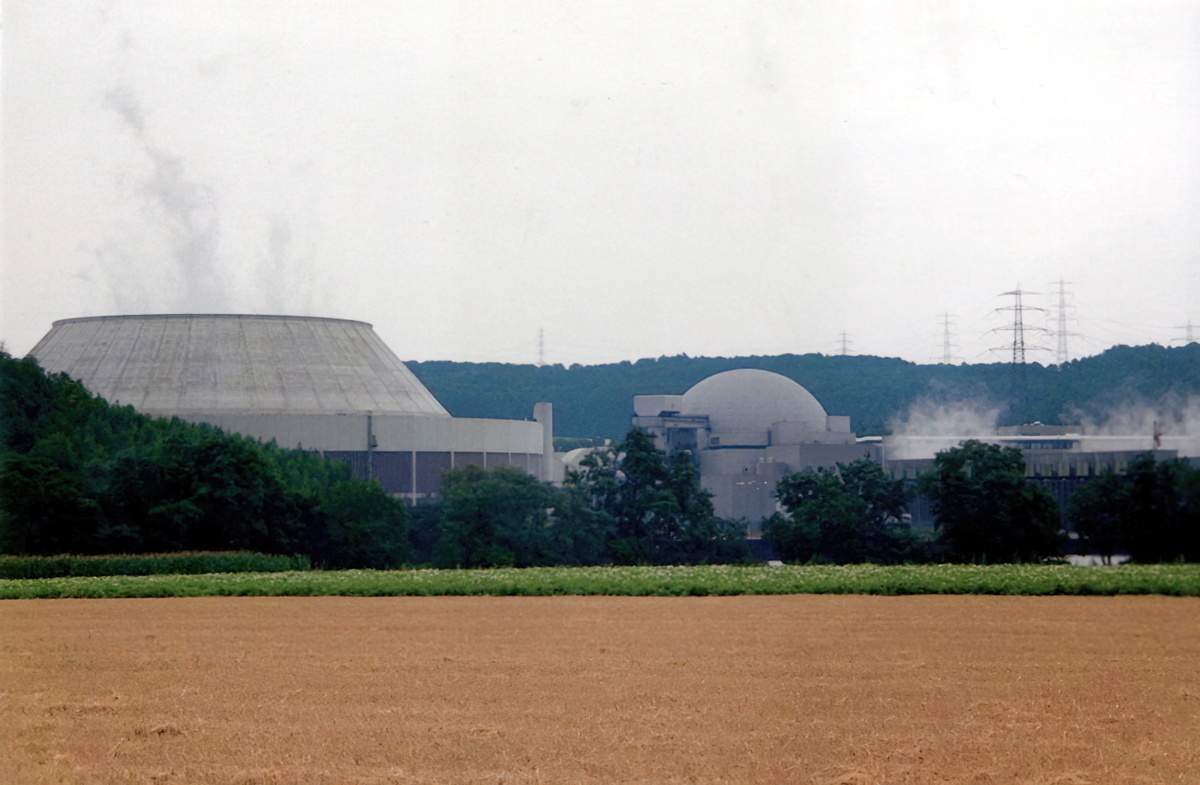

(Source: Michael Meding [CC BY-SA 2.0 DE], via Wikimedia Commons.)
Because of concerns over safety, people in Germany have been protesting against nuclear power since the 1970s. In 2000, the government approved a plan to shut down its nuclear power stations, but the plan was later stopped.
In 2011, a nuclear plant in Fukushima, Japan was hit by a massive earthquake and tsunami, causing the world’s worst nuclear accident since 1986.
After the Fukushima disaster, Germany’s government approved a plan to shut down all of its nuclear power plants by 2022. Eight nuclear stations were shut down soon afterward. The remaining nine were meant to be shut down by the end of 2022.
That plan was slightly delayed because of Russia’s war on Ukraine. Germany used to get 55% of its natural gas from Russia. Last year, it stopped buying Russian fuel in response to the invasion of Ukraine.
(Source: Chart: Clean Energy Wire, data: BDEW [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons.)
Without Russian gas, there were concerns that Germany might not have enough fuel to make it through the winter. So Germany delayed shutting down its last three nuclear plants until April 15.
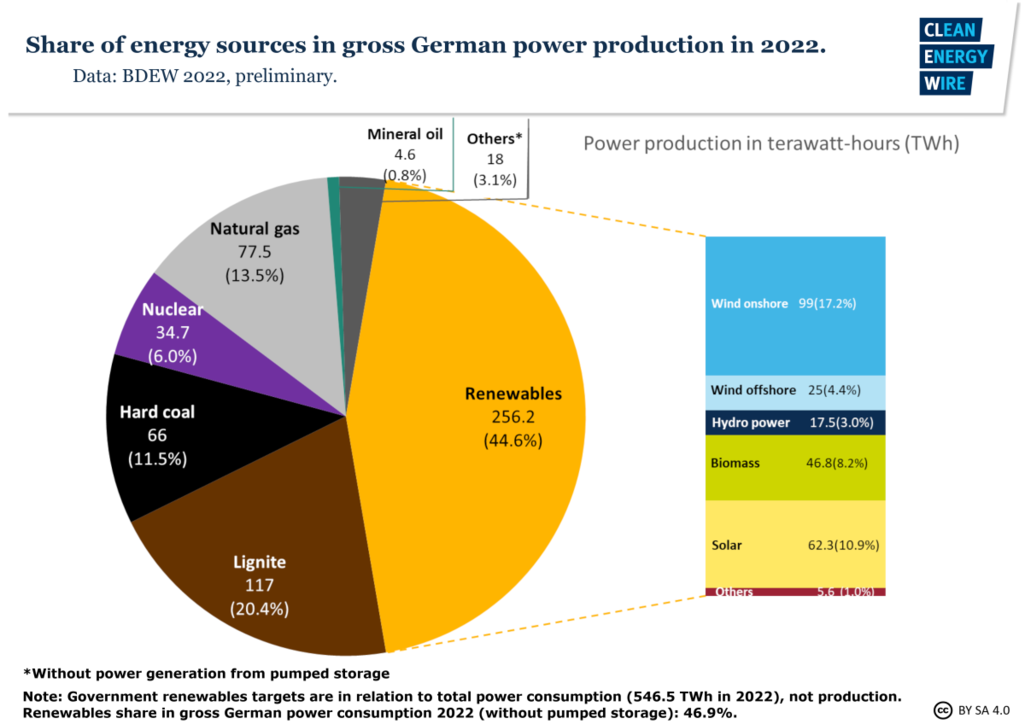
In recent years, nuclear power has provided less and less of Germany’s electricity. In 2000, it supplied about 30% of Germany’s electricity. By last October, that number had fallen to 6%.
Cutting back on nuclear power meant Germany had to find other ways to make electricity. Germany has been adding more and more wind and solar power. But it has also used more coal and natural gas.
The nuclear plants are now officially closed, but not everyone agrees with the move. In a recent survey, 52% of Germans were against shutting down the nuclear program.
😕
This image has not been loaded because of your cookie choices. To view the content, you can accept 'Non-necessary' cookies.
The nuclear plants are now officially closed, but not everyone agrees with the move. In a recent survey, 52% of Germans were against shutting down the nuclear program. Above, the Emsland nuclear power plant last Saturday, the day the plant was officially shut down.
Some people say it was a waste to shut down power plants that were producing cheap energy. Others worry that without nuclear power, Germany will use more fossil fuels and pollute more. Also, nuclear plants can provide energy constantly. Many renewable energy sources only work some of the time – like when it’s windy or the sun is out.
Robert Habeck, a member of Germany’s Greens party, believes any increase in fossil fuel use won’t last long. “We will have 80% renewable energies by 2030,” he says.
Some experts point out that nuclear power can also be affected by weather conditions. The droughts and extreme heat in Europe last summer forced several nuclear power plants to stop working because there wasn’t enough cold water to cool them.
And there are still safety concerns. Russia’s attacks on Ukraine’s nuclear power stations have been a strong reminder of the risks that come with nuclear power.
Many people will be watching Germany closely to see whether its decision to end its nuclear power program was a good choice or a poor one.
