Antarctica —(Map)
Scientists have reported that Antarctica’s sea ice is at a record low level. That’s worrying because the sea ice is an important part of the Earth’s cooling system. It’s not yet clear if the low sea ice level is temporary, or part of a changing climate pattern.
Antarctica is a great, icy land mass, surrounded by the huge Southern Ocean. The ice in Antarctica doesn’t just cover the land. There’s also a massive area of sea ice, which floats on the ocean’s surface.
Every year, the sea ice at the South Pole goes through a cycle of melting and freezing. In the summer, the huge masses of sea ice melt to their smallest point. Over the colder winter months, the sea ice grows and grows until it covers an incredibly wide area. Usually, the sea ice covers the greatest area (its “maximum extent”) around September 23, as winter ends at the South Pole.

(Source: Nathan Kurtz/NASA ICE [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons.)
Scientists have been measuring the area of the sea ice in Antarctica since 1979. For most of this time, Antarctica has seemed to be almost unaffected by the changing weather conditions experienced in other parts of the globe. In fact, until recent years, Antartica’s sea ice area mainly set records for growing.
That began to change around 2016. Now, for several years, the area of Antartica’s sea ice has been shrinking.
This year, the US National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) reports that Antartica’s sea ice reached its maximum extent on September 10 – almost two weeks earlier than normal. And the sea ice was at a new record low – not just by a little bit, but by a lot.
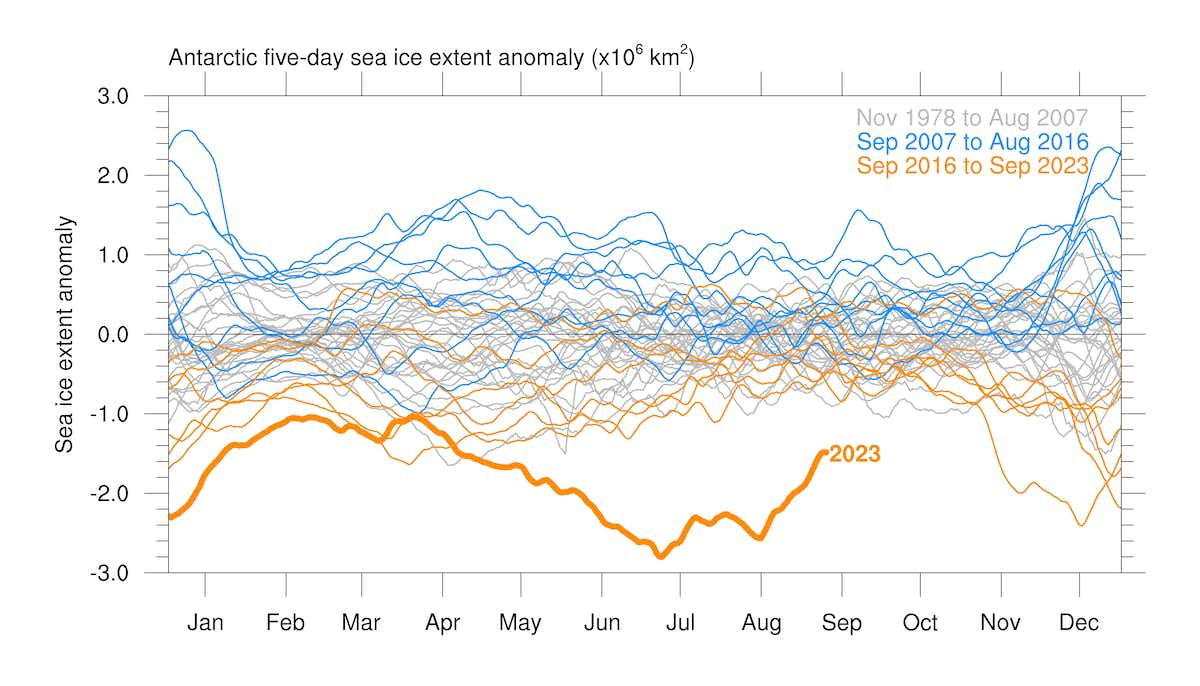
(Source: Ariaan Purich [CC BY-SA ], via TheConversation.)
The last time Antartica’s low sea ice set a record at the end of winter was in 1986. And this year, there’s about 398,000 square miles (1.03 million square kilometers) less sea ice than in 1986. It’s hard to picture that large an area, but it’s roughly 1.5 times the size of the US state of Texas, or 1.6 times the size of France.
Scientists are still trying to understand what is driving the change in Antarctica. One likely cause for the change is the rising temperatures of the world’s oceans. Ted Scambos, a research scientist at the University of Colorado, says Antarctica’s ice levels have always changed some, but the sharp loss this year is “pointing towards warmer ocean conditions around the continent.”
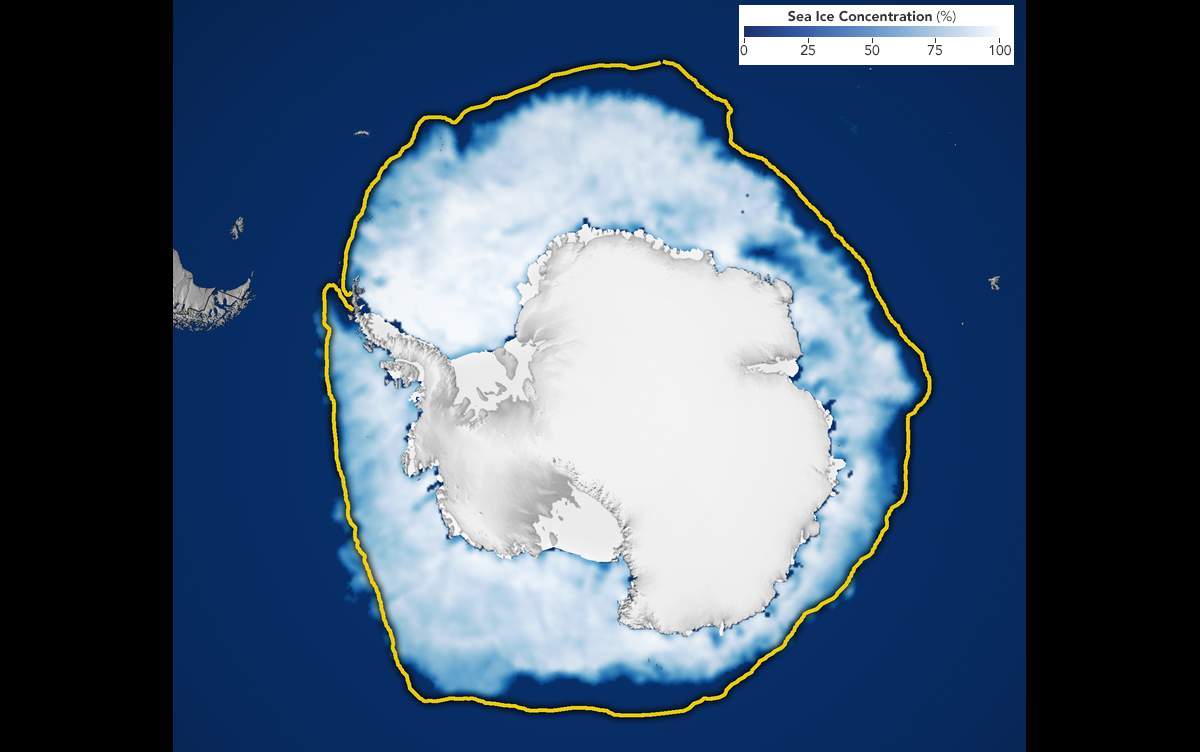
(Source: Lauren Dauphin/NSIDC, via NASA Earth Observatory.)
The new low record has scientists worried. The sea ice is important, because it helps cool the planet. When it’s frozen, sea ice reflects sunlight back out into space. But when the sea ice melts, the water left behind is darker, and absorbs more heat. The concern is that the melting sea ice could start a cycle that might cause even more ice to melt.
Scientists are working hard to better understand Antarctica. They don’t know yet if this is just a short-term problem, or if it’s part of a long-term shift toward less sea ice in Antarctica.
Did You Know…?
The ice loss problems in Antarctica are fairly recent, but the same is not true at the North Pole, where the low level of sea ice has been a concern for years. But the current situation is now similar in both places. The amount of sea ice in the Arctic at the end of this summer was the sixth lowest ever recorded.
😕
This map has not been loaded because of your cookie choices. To view the content, you can accept 'Non-necessary' cookies.
